Configuring modems with
Windows 3.1 and
Netscape Dialers
Three types of settings are important with respect to modem configurations:
COM ports, IRQ's, and IO addresses.
These settings must match on the modem itself, the Netscape Dialer and in the Windows Control Panel.
COM ports and IRQ's can be changed on most modems via pins on the board. Since most mice are set up on COM1, IRQ4, it is recommended to set the modem on one of the following combinations:
- COM2, IRQ3 (by default)
- COM3, (with an IRQ other than 4)
- COM4, IRQ3 (by default)
Most Packard Bell computers and some others have mice set to COM2, IRQ3. In any event, don't set a modem on the same IRQ as the mouse, at this will cause the mouse to freeze. If the customer is setting a modem on IRQ5, ask if the customer has a Sound Blaster 16 card. Most Sound blaster cards use IRQ5 as default.
Use Microsoft Diagnostics to find what settings the computer is reading from the modem. Windows must be exited altogether, then type msd at the DOS prompt. After clicking "COM Ports...", the following appears:
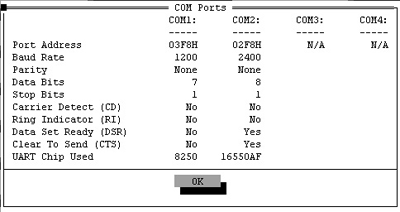
The above shows that a modem is on COM2, since there is a 16550 UART associated with it, and DSR and CTS is set to "Yes". The IO address is shown as 02F8h on COM2. Don't worry about the baud rate (2400). It is overwritten by the communication software.
Match the settings in Control Panel. From Program Manager, click Main, then Control Panel, then Ports. The following appears:
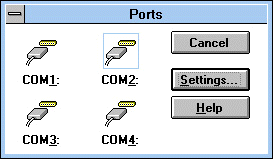
Highlight the COM port the modem is on (COM2 in this case), and click Settings.
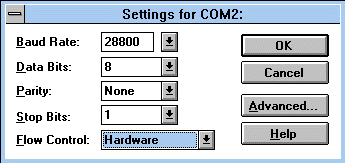
Don't worry about baud rate setting in this window. This setting is overwritten by the communication software. Data Bits, Parity, and Stop Bits are 8, None, and 1 by default. Flow Control should be hardware based. If it is Xon-Xoff, change it to Hardware. Click Advanced and you will see:
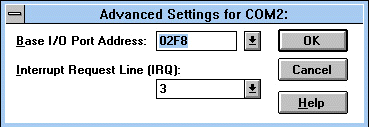
Match the port address with the results from MSD. The IRQ should match the IRQ set by the customer on the modem board. Remember the even-odd, odd-even rule: Even numbered COM ports should match with odd numbered IRQ's. Odd numbered COM ports should match with even numbered IRQ's.
Match the settings with the Netscape Dialer. Open Erols Dialer, and the following appears:
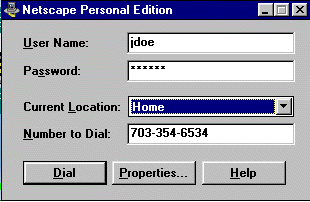
Click Properties, then click the Modem tab at the top of the window:
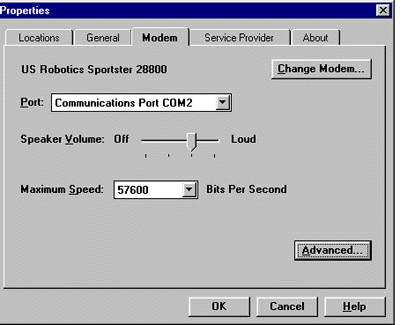
Change the COM port and baud rate if necessary. Click Advanced:
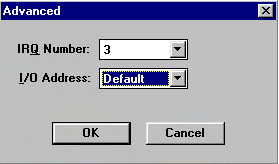
Match the IRQ to the Control Panel setting. If I/O address is listed as Default, change it to match the setting in Control Panel.
As a general rule:
- COM1: 03F8h
- COM2: 02F8h
- COM3: 03E8h
- COM4: 02E8h
Modem problems:
If the modem selected by the dialer doesnít work correctly, open the Dialer, choose Properties, and choose the Modem tab. Choose Change Modem. Check Donít detect my modem, let me specify it. Click Next, and the following appears:
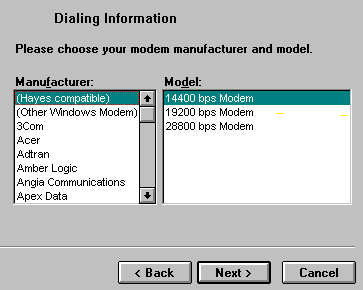
Try Hayes compatible 14400 or 28800 bps modem. These are generic initialization strings which work with most hardware based modems.
RPI or software based modems:
If you have an RPI (Rockwell based) modem, try choosing a Rockwell based string (Netscape 2.01 shown). PCMCIA modems are for laptops only.
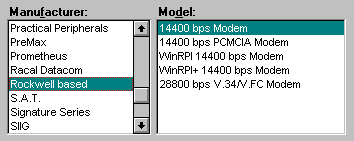
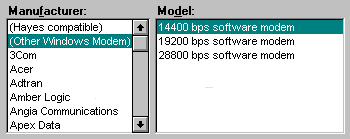
If this doesnít work, try Other Windows modem, as shown below (Netscape 2.01 Dialer only).
Testing for an RPI modem :
- If the letters RPI do not appear on the modem box, look for the word Rockwell, or the phrases: software based error control, or software based flow control, either on the box, or anywhere in the instructions. Also look for Windows software included.
- All RPI modems are cheaper than hardware based modems. If you paid $30.00 for a 28800 modem, it is probably RPI.
- Open Windows Terminal from the Accessories Group. Choose Settings, then Comunications. Match the COM port to the modem, click ok.
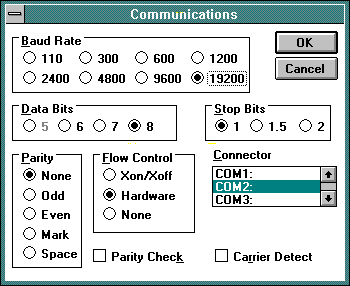
Type ATI3 and hit enter at the prompt. The name or identification number of the modem should appear. An RPI modem should return with a name including Rockwell, RPI, or RPI+. Take note that not all modems respond to this command. Try ATI 3.
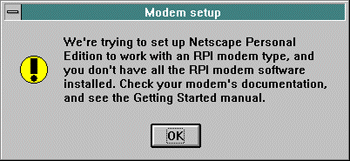
If you get this response below , the Dialer cannot find the software needed to run the modem (usually WinRPI). This software either comes with the modem, or is installed with a communications program.
If you have a way-off-brand modem, but you happen to know the initialization string, you can try editing the modem file. Click File from Program Manager, then Run. Type: notepad c:\netscape\dialer\modems2.ini then click on OK.
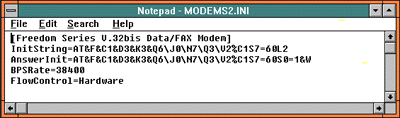
Replace the InitString and AnswereInit (between the first two equal signs) with your own strings, change BPSRate, etc., then save the file. A typical hardware modem ini is shown above. Below is a typical RPI ini.
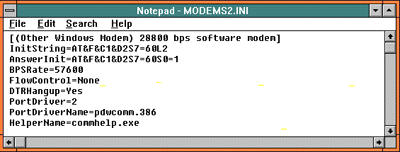
In any case the changes stick as long as you stay with this modem string. If you pick a new modem by way of the Change Modem button, the edited string will be lost and will be replaced by the original strings. No harm done.
Home | Common Issues | Navigator 1.22 Installation | Navigator 2.01 Installation














