diagram courtesy Dr. Bill Hodson
Artificial Intelligence (AI) could be defined as the ability of computer software and hardware to do those things that we, as humans, recognize as intelligent behavior.Traditionally those things include such activities as:
Searching:
finding “good” material after having been provided only limited direction,
especially from a large
quantity of available
data.
Surmounting
constraints: finding ways that something will fit into a confined
space, taking apart or building a
complex object, or
moving through a difficult maze.
Recognizing
patterns: finding items with similar characteristics, or identifying
an entity when not all its
characteristics are
stated or available.
Making
logical inferences: drawing conclusions based upon understood reasoning
methods such as deduction
and induction.
AI technologies extend from the word Technology which stems from the Greek word technos, which means "art" and "skill." A sophisticated technology is then a cumulative building of learned and well-refined skills and processes. In the AI area, these processes have manifested themselves in a number of well-recognized and maturing areas including Neural Networks, Expert Systems, Automatic Speech Recognition, Genetic Algorithms, Intelligent Agents, Natural Language Processing, Robotics, Logic Programming, and Fuzzy Logic.
Each of these areas will be examined in some depth here, but it is first important to understand that the importance of these individual areas has changed over the last two decades. These changes have been based upon the progress in each area, and the needs that each area meets. For example in the early 1980’s robotics was a large thrust in artificial intelligence. At that time benefits could be seen in manufacturing applications. In the late 1990’s the blossoming of the Internet pushed the importance of intelligent agents forward for performing routine tasks and complex searches. At the same time, throughout the 1980s and 1990s, orders of magnitude advances in computer processing power have allowed hurdles in speech recognition and image processing to be overcome.
The maturity of each of these technology areas also differs. Expert Systems and Automatic Speech Recognition are among the most mature while Natural Language Processing and Intelligent Agents remain in early stages of development. In the next few paragraphs the basis for each of these technologies will be reviewed. In addition examples where the technologies have been effectively utilized will be presented.
The Neural Network
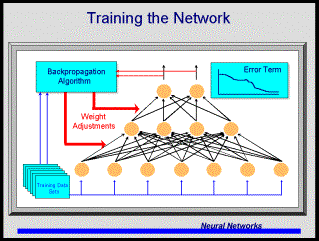
This technology is based loosely upon the cellular structure of the human brain. Cells, or storage locations, and connections between the locations are established in the computer. As in the human brain, connections among the cells are strengthened or weakened based upon their ability to yield "productive" results. The system uses an algorithm to “learn” from experience. Using a tree identification system as an example, the diagram and process below demonstrates how a simple neural network operates. The outputs (top 2 circles) of this system are tree types - conifer (left circle) and deciduous (right circle). The inputs (bottom 7 circles) are tree characteristics such as color, shape, leaf type, bark type, etc.

diagram courtesy Dr. Bill Hodson
1) From a training set, a single example's characteristics, e.g. dark green, triangular, needle, and scaly are fed into the bottom of the system. Typically each of the many characteristics are identified simply as a 0 or a 1, where for example the first characteristic, color, a 0 would mean dark green and a 1 would mean light green.
2) In the middle layer shown above, the 0's and 1's are combined and pushed up through the system using summation and transfer algorithms.
3) Upon reaching the top a 1 would appear in the left circle, identifying a conifer or a 1 would appear in the right circle, identifying a deciduous tree. If the answer was correct, in this case a 1 in the left circle, the connection strengths would be increased. Weights would be adjusted upward. If the answer was incorrect, in this case a 0, the connection strengths would be decreased.
4) This process (1-3 above) is repeated many times, using a different case, e.g. light green, circular, broad leaf, and smooth each time.
Eventually the error, that is producing a zero as an output when it should be producing a one, is reduced to a state where it is almost always “right.” This is the learning that takes place. After sufficient learning, it has the ability to identify or classify “similar” cases - although it may have never seen the combination of characteristics before. It has “stored” the knowledge of the examples it has seen. Neural nets are an inductive reasoning method.
Neural Networks are used today for helping to identify the presence or absence of certain types of explosives in checked airline baggage. As the baggage passes through a special scanner, the scanner “sniffs” out the explosives by bombarding the luggage with harmless atomic level particles. The system then passes the pattern produced through the neural network that has been trained to see the peculiar patterns of the explosives.
Expert Systems
These systems are usually built using large sets of “rules.”An expert, who has developed them mentally after perhaps a decade or more of practice in a specialty area, establishes these rules. A specialist, known as a knowledge engineer, extracts the rules from the expert and programs them into a computer. An example of a small rule set follows.
IF the relief pressure valve is less than .25 open and the pressure setting is greater than 160 kg,Expert Systems are established for processes where there is a need;
THEN pressure-category is high.
IF then temperature is less than 250 centigrade,
THEN category is normal,
ELSE temperature-category is hot.
IF pressure-category is high and temperature-category is hot,
THEN send operator alert.
1) for a narrow area of expertise
to be more widely known, or
2) to allow sophisticated processes
to be run without human intervention.
A classic example of the former is a need for understanding and interpreting the rules of code and regulations set forth by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service. To provide benefit to the average citizen preparing their taxes, these rules are programmed into popular software packages such as Tax Cut and TurboTax. A classic case of the second need is a back end system programmed by the Credit Card Division of the American Express Company. This system uses sophisticated rules to determine whether a credit transaction should be approved, denied, or be interrupted by human intervention.
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
This technology takes the sound waves produced by our speech and converts them into text content. The process, made possible by lots of computer memory and fast processors, works like this:
Genetic Algorithms
To evaluate and locate the best candidates for a task, the Genetic Algorithm (GA) has been found to be a very effective method . GA's borrow from scientific discovery about the evolutionary nature of our genes. They utilize fitness functions, which are relationships among criteria, to grade candidates. They also use evolutionary methods such as crossover and mutation on chromosomes, or strands of information, to find the best examples from a very large field of possibilities. This amazing technology provides the capability to find a needle in a haystack. GA's use a method known as abductive reasoning. This method boils down to sophisticated trial and error.
How does a detail genetic algorithm process work? It follows 5 simple steps
1. evaluate the population against "high fitness"
criteria;
2. if a candidate in the population meets the criteria
stop, else
3. select the best of the current set using a selection
strategy and diversity maintenance, then
4. reproduce using crossover & mutation, and
5. return to 1
Population - candidate/possible solutions to a problem
Selection Strategy - strategy for selecting chromosones to move forward
in current cycle
Diversity Maintenance- strategy for assuring that generations do not
get caught in local minima
Crossover - part of one chromosone is combined with another through
mating
Mutation - random alteration of a gene
High Fitness Criteria - an "ideal" candidate
Genetic Algorithms have been used to help police work with witnessess to quickly narrow down the possible perpetrators of a crime. They use a system known as FACEPRINTS. Manufacturers, such as Deere and Company, utilize GA's to help them set up schedules that combine a large and complex set of constraints. And General Electric has used a GA approach to help them tune aricraft engines, which can lead to a significant increase in efficiency.
Intelligent Agents
Intelligent agents (IA), now often known as "bots", are software technology that performs difficult or repetitive tasks for a user. Using direct commands or on a scheduled timetable, the IAs execute a provided list of instructions known as a script. The intelligent agent technology typically “borrows” from capability inherent in other AI techniques, especially in the area of search. The IA capability can then add the “ever diligent” capability provided to us by computer processors that can stay awake and work 24 hours a day 7 days a week. A simple script follows that checks for stories about the stock market and then notifies the user via e-mail when one of interest appears.
When HOUR = (11:00 or 13:00 or 15:00 or 16:30)Scripts that are well crafted can perform actions such as periodically:
Start ieexplorer.exe
Load URL = http://www.msn.com
Search site for text = "DJIA"
If present THEN
Start outlook.exe
Address = saunders@ndu.edu
Subject = "Story on Dow Jones Industrial Average"
Body = "At HOUR There was a story on the DJIA posted on the MSN Web site. Click here to retrieve it"
Else END
Checking for a stock price to hit a certain level and then executing a buy or sell at that price.Intelligent agents take many forms. The web site http://www.botspot.com lists the following general categories
Checking a web site to see if any new documents have been deposited.
Chatter Bots
Commerce Bots
Data Mining Bots
E-Mail Bots
Fun Bots
Game Bots
Government Bots Knowledge
Bots
Miscellaneous Bots
News Bots
Newsgroup Bots
Search Bots
Shopping Bots
Software Bots
Stock Bots
References
General
PC AI Magazine http://www.pcai.com/pcai/
American Association for Artificial Intelligence
http://www.aaai.org/
Specific Area Links
Expert Systems http://users.erols.com/jsaunders/guides/experweb.htm
Neural Networks http://users.erols.com/jsaunders/guides/nn.htm
Genetic Algorithms http://users.erols.com/jsaunders/guides/ai.htm
Intelligent Agents http://users.erols.com/jsaunders/guides/agents.htm
Mini Quiz
Now that you have read about each, can you match the technologies to
the type of task they are best suited?
| ____ Neural Networks,
____ Automatic Speech Recognition, ____ Natural Language Processing, ____ Genetic Algorithms, ____ Expert Systems, ____ Intelligent Agents, ____ Robotics, ____ Logic Programming ____ Fuzzy Logic |
a. Searching
b. Surmounting constraints c. Recognizing patterns d. Making logical inferences |
Answers. c.,c.,a.,b.,d.,a.,b.,d.,d.
(c) May 2000 John H. Saunders