

NetBSD Quick Guide
Username and Passwords:
If you have networking configured already, your NetBSD box may be accessed remotely using a secure shell(ssh) client if you used my CD install. Secure shell access by root is O.K., but telnet won't allow it for security reasons. You need to add a user other than root to use telnet or ftp.
File Editing:
To edit the files on the NetBSD firewall system you will want to use the vi editor. Here are a few key commands to get you started:
vi filename — opens the file filename in the vi editor.
arrow keys — move up and down through the document
editor commands:
esc — ends execution of the current command; must be pressed to use the arrow keys or execute another command.
i — inserts a character at the cursor.
x — deletes a character at the cursor.
dd —deletes an entire line at the cursor.
esc, q! — quits without saving changes.
esc, wq! — saves the file and quits.
Network Interfaces:
The network interfaces are generally ae0 or sn0 depending on you ethernet card. Type dmesg | fgrep ae0 or dmesg | fgrep sn0 and hit return at the prompt to display your card. If you have more than one card, you may see ae0 and ae1. You should see something like:
ae0 at nubus0 slot d: MacCon Ethernet, 32KB memory
ae0: Ethernet address 00:00:94:21:30:5e
See the following diagram on how to configure your card's IP address.
Important network configuration files include:
Password Management:
I recommend you change the default passwords assigned to the system. Do this by executing the command "passwd" as root. The prompts will ask you for your new password. Do not forget it or you won’t be able to get into your NetBSD box and will have to boot into single user mode to reset your password.
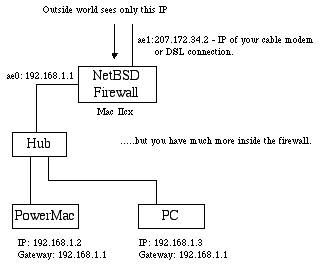
Firewall Internet Traffic on Your Home Network:
You can easily protect your home network from would-be hackers by using NetBSD as a firewall to filter the traffic. A typical setup is shown below. While your setup may vary, the idea is still the same.
Need more help. Good help documents can be found online at: http://www.erols.com/ewinkler.